Gynecological ultrasound
We perform the following pelvic ultrasound scans:
Transabdominal ultrasound scans Transvaginal ultrasound scans Transvaginal and transabdominal ultrasound scans of patients with suspected malignancies Follicle growth ultrasound tracking Ultrasound pelvic scans using saline solution in order to assess the uterine cavity Fallopian tube patency assessment using Air-Sono; HyCoSy techniquesAt present, we conduct examinations with the use of a Samsung WS80 Elite, a GE Voluson E8, as well as a Voluson 730.
Transabdominal ultrasound scans
This kind of scan is performed on girls and women who have not yet become sexually active or as a complementary examination in case when transvaginal ultrasound is unsatisfactory.
It is essential to understand that the image resolution in transabdominal ultrasound is lower, therefore, a patient should be adequately prepared. In order to make the uterus and its adnexa (i.e. mainly ovaries) visible, it is necessary to fill the bladder. The patient should drink 1L of still water 30 minutes before the examination.
We would like to provide young patients with maximum comfort, for this reason, we assure you that young girls who have not had sexual intercourse yet, will not undergo transrectal scan at our centre. In each case we spare no effort to clarify questionable issues through transabdominal ultrasound. At our centre, this type of examination is performed by dr. Agnieszka Nocun and dr. Marcin Wiechec. If it is important for a patient to be examined by a woman, please mention it during the registration.
Similarly to transvaginal ultrasound, we measure the length, breadth and thickness of the uterine body, endometrial thickness, the length, width and thickness of ovaries, the size of potential abnormalities and the blood flow in the uterus and ovaries if necessary. We also assess the myometrial-endometrial junction, the relationships between pelvic organs and the topographic anatomy of abnormalities in reproductive organs.




Transvaginal ultrasound scans
It is a detailed scan of the reproductive organ, in which special attention is paid to the uterus and its adnexa; recto-uterine pouch, which is the extension of the peritoneal cavity between the rectum and the posterior wall of the uterus; and the walls of the bladder. We measure the length, width and thickness of the uterine body, endometrial thickness, the length, width and thickness of ovaries, the size of potential abnormalities, and the blood flow in uterus and ovaries if necessary. We also assess the myometrial-endometrial junction, the relationships between pelvic organs and the topographic anatomy of abnormalities in reproductive organs.
We perform this kind of scan with a regular use of two-dimensional and three-dimensional ultrasound as well as the dynamic examination, which allows to analyze the reproductive organ mobility and possible pathological changes.
Transrectal scan is performed only in rare cases, e.g., in patients with advanced cervical cancer.




Transvaginal and transabdominal ultrasound scans of patients with suspected malignancies
We are experienced in examining reproductive organs in patients with suspected or identified malignancy. In such a case, the ultrasound scan should be conducted by a skilful sonologist. It is essential to assess minor pelvis region during transvaginal scan (in rare cases also during transrectal scan) as well as abdominal cavity and the retroperitoneal space in transabdominal scan.
In transvaginal scan we inspect reproductive organs, i.e. cervix and body of the uterus, its adnexa, rectum, rectovaginal septum, parametric, vesico-vaginal septum, urinary bladder and urethra. While assessing focal lesions, not only do we measure them, but also estimate the extent of the abnormalities. We perform two- and three-dimensional ultrasound examinations as well as dynamic examination.
In transrectal scan we also inspect potential vaginal and rectal infiltration.
In transabdominal scan we seek potential metastases or cancer recurrence, in case of an extensive abnormality, we precisely estimate its size and extent.




Follicle growth ultrasound tracking
Follicle growth tracking is a series of ultrasound scans, which are performed in order to confirm ovulation. We start between the 7th and the 9th day of a cycle, and we begin with estimating the growth of the follicle(s) per day. The series is finished in case of confirming the ovulation or not. In the ovulation cycles during consecutive examinations we observe the follicle growing gradually, and the process in which it ruptures leaving stigma in the ovary i.e. a place of a corpus luteum origin.
Ovulation monitoring is performed in natural cycles as well as in those stimulated by medicines in cooperation with a gynecologist in charge.


Ultrasound pelvic scans using saline solution in order to assess the uterine cavity
Some of abnormalities are difficult to explain during an ordinary transvaginal ultrasound scann. They have to be verified through Saline Infusion Sonography. This method involves placing a catheter stent (the diameter of the catheter stent should be comparable to the natural width of the cervical canal) into the cervical canal. Then, through a catheter stent we administer a small amount of saline solution. Owing that, the uterine cavity is relaxed and allows for ultrasound scan.
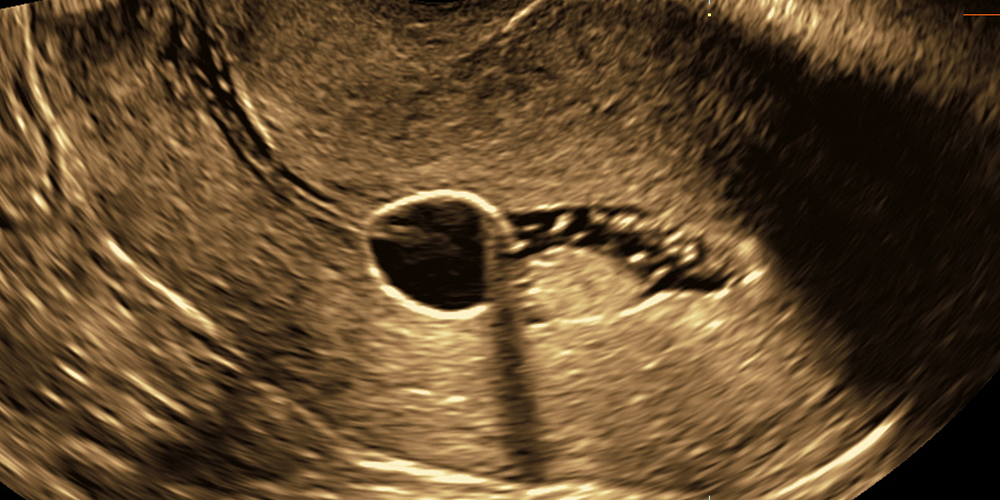

Fallopian tube patency assessment
Fallopian tubes patency is one of the basic conditions indicating fertility of a woman. Its dysfunction is classified as one of the most frequent causes of infertility. Different methods of assessing Fallopian tubes patency are employed. Ultrasound methods are comparable with X-ray (HSG), however, the discomfort of a patient during ultrasound assessment is lower. We use two methods:
Air-sono – American method consisting in contrasting saline solution with air which gives a white ultrasound image of the uterine cavity and Fallopian tubes.
HyCoSy – using Exem foam contrast (innovative, safe, the most efficient contrast for Fallopian tubes assessment, sustaining long enough to perform an examination in three-dimensional techniques).
The technique consists in placing a thin catheter stent (with the diameter of the catheter stent comparable to the natural width of the cervical canal) into the cervical canal. Next, through the catheter stent we administer the contrast or a small amount of a saline solution interchangeably with air. The scan is additionally stored and analyzed directly after its completion.
See the clip below demonstrating right tubal patency (bright linear structure on the left side of the screen) together with left tubal obstruction (lack of the bright linear structure on the right side of the screen).
